
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Monday Jan 26 2026 10:11

18 min

CFD Trading Basics: Contract for Difference (CFD) trading is a popular method for speculating on price movements in various financial markets without owning the underlying asset.
Understanding the basics of CFD trading requires not only a grasp of how these instruments work but also an appreciation for fundamental analysis. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of CFD trading, focusing specifically on the principles of fundamental analysis and its application in trading strategies.
A Contract for Difference is a financial derivative that allows traders to speculate on the price changes of various assets, including stocks, commodities, indices, and currencies. With CFDs, traders can take positions based on whether they believe the price of the asset will rise or fall.
When a trader enters a CFD, they agree to exchange the difference in the asset's price from when the contract is opened to when it is closed. If the trader predicts the price increases, they would buy the CFD (going long). Conversely, if they expect the price to decline, they would sell the CFD (going short).
Leverage in CFD Trading
One of the defining characteristics of CFD trading is the use of leverage. Leverage allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. For instance, a broker may offer a leverage ratio that allows a trader to control a position of 100,000 units with only 1,000 units of their capital. While leverage can amplify gains, it also increases the risk of substantial losses.

Benefits of Trading CFDs
Access to Global Markets: CFDs provide access to a wide range of financial instruments, including global indices, commodities, and currencies.
Short Selling: CFDs allow traders to profit in falling markets by enabling short selling without needing to locate and borrow the asset.
No Stamp Duty: In some jurisdictions, CFD trading does not incur stamp duty since the investor does not own the underlying asset.
Flexibility: Traders can take both long and short positions, giving them the flexibility to strategize based on market conditions.
Risk Management Tools: Many brokers offer various risk management tools like stop-loss orders to help traders manage their exposure.
What is Fundamental Analysis?
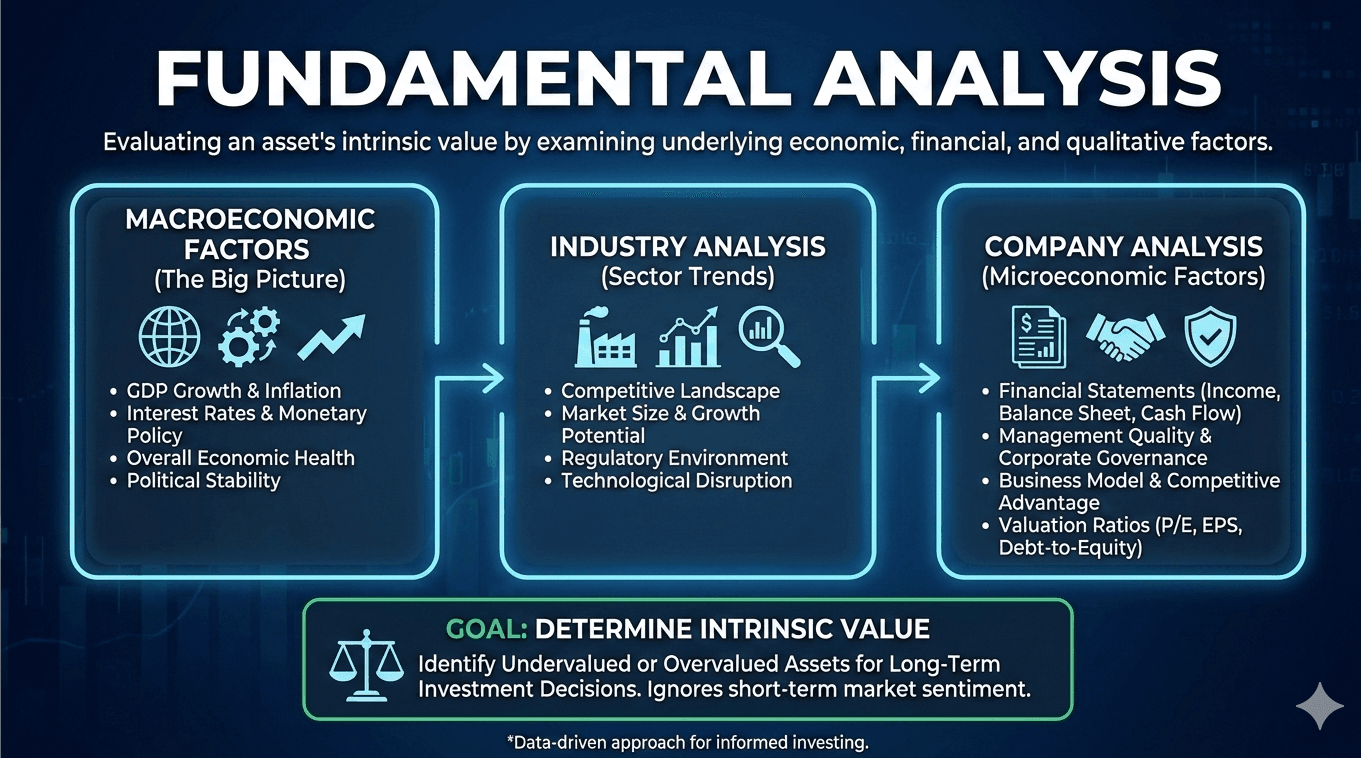
Fundamental analysis is a method of evaluating an asset’s value by studying the economic, financial, and other qualitative and quantitative factors that may affect its price. The goal is to understand the intrinsic value of an asset and its potential for growth or decline.
Key Components of Fundamental Analysis
Economic Indicators: These are statistics that gauge the economic performance of a country and can significantly influence asset prices. Key indicators include GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation.
Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, which directly affect the cost of borrowing and the profitability of investments. Changes in interest rates can trigger significant moves in the markets.
Corporate Financial Health: For equity CFDs, analyzing a company's financial statements—such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements—can provide insights into its profitability and solvency.
Market Sentiment: Understanding investor sentiment, often influenced by news events, geopolitical developments, and economic reports, is vital for predicting price movements.
Political Environment: Political stability and policies can affect market conditions. Changes in government, regulation, or international relations can lead to volatility.
Sources of Economic Data
Government Reports: National statistics agencies publish a wealth of economic data, including labor market statistics, GDP figures, and trade balances.
Central Bank Publications: Central banks frequently provide insights into monetary policy and macroeconomic forecasts, which are crucial for evaluating interest rates.
Financial News: Reliable financial news sources report on events that may impact the financial markets and provide expert opinions and analyses.
Economic Calendars: Many trading platforms offer economic calendars that outline key upcoming economic indicators and news releases, allowing traders to plan their strategies effectively.
Analyzing Economic Indicators
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A growing GDP typically indicates a thriving economy, which can boost investor confidence and drive asset prices upward.
Inflation Rates: High inflation can erode purchasing power and may lead central banks to increase interest rates, affecting market dynamics.
Employment Data: Strong employment figures suggest economic health, while rising unemployment can signal problems within an economy.
Consumer Confidence Index (CCI): A rising CCI indicates greater consumer optimism, which can lead to increased consumer spending and economic growth.
Evaluating Corporate Performance (For Equity CFDs)
When trading CFDs based on individual equities, understanding a company's performance is crucial.
Earnings Reports: These reports divulge the company's revenue, profit margins, and expenses. A positive earnings surprise can lead to an immediate price increase, while a disappointing report can lead to declines.
Balance Sheets: A company’s balance sheet provides insight into its financial health, including its assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. Analyzing key ratios like the debt-to-equity ratio helps gauge risk.
Cash Flow Statements: These provide insights into how a company generates cash and manages its liquidity. Healthy cash flow is a sign of a well-managed company capable of sustaining operations and funding growth.
Market Position and Strategy: Assessing a company's competitive positioning within its industry, analyzing market share, and evaluating strategic initiatives can provide insights into longer-term growth potential.
Defining Your Goals
Before embarking on CFD trading, it's essential to establish clear trading goals. Are you looking for short-term gains or long-term investment opportunities? Your approach will influence how you conduct fundamental analysis and make trading decisions.
Short-Term Trading: If your goal is to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations, you’ll need to pay close attention to economic announcements and news that can trigger volatility.
Long-Term Investing: A longer-term approach may involve more extensive research into fundamental indicators and a comprehensive analysis of market trends. Patience often pays off in longer-term positions.
Combining Fundamental Analysis with Technical Analysis
While fundamental analysis focuses on economic and financial data, technical analysis examines price patterns and market trends. Many successful CFD traders adopt a hybrid approach, integrating both fundamentals and technical indicators to enhance decision-making.
Technical Indicators: Familiarize yourself with key technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, and MACD, which can help identify market trends and potential reversal points.
Chart Patterns: Learning to recognize chart patterns, such as head and shoulders or support and resistance levels, can complement your fundamental analysis by providing entry and exit signals.
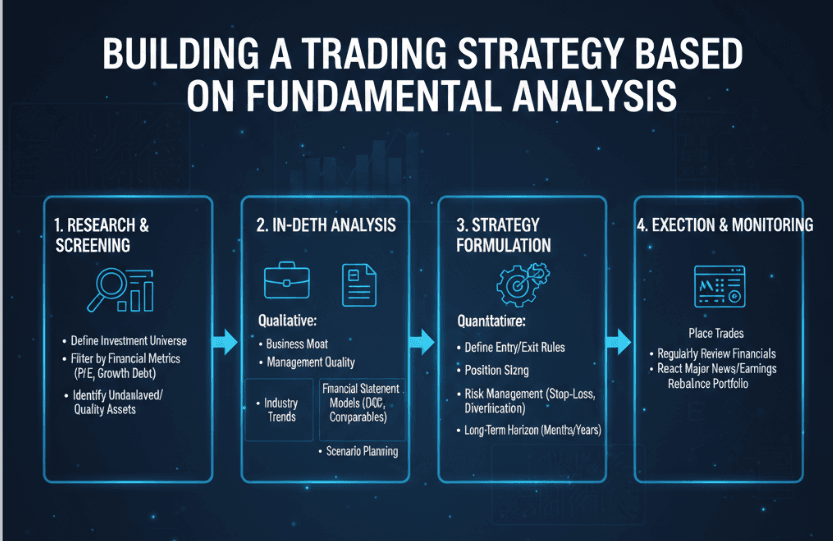
Identifying Key Events
Keep an eye on major economic events that are likely to influence asset prices. For example, interest rate announcements, legislative changes, or significant macroeconomic reports can lead to substantial market volatility. Understanding the potential impact of these events can help in positioning trades effectively.
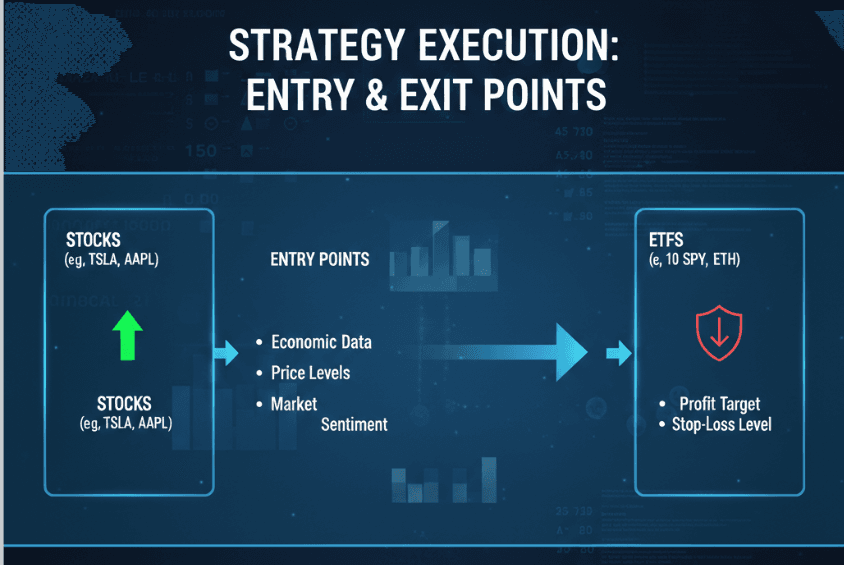
Formulating Entry and Exit Strategies
Based on your analysis, develop entry and exit strategies. Clearly define your entry points based on favorable economic indicators and sentiment while also establishing exit points to secure gains or limit losses.
Risk Management
Implementing a robust risk management plan is imperative in CFD trading. Determine your risk tolerance, set stop-loss orders, and consider diversifying across multiple assets to mitigate risks.

When trading equity CFDs, focus on the underlying business's performance and the industry conditions. Key metrics include earnings reports, revenue growth, and competitive positioning.
Commodity CFDs
For commodity CFDs, study supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical factors, and currency fluctuations. For instance, oil prices may be influenced by OPEC decisions, while agricultural products can be affected by weather conditions.
Supply-Demand Factors: Understand the balance of supply and demand in the market. For example, excessive supply in the oil market could lead to falling prices, while increased global consumption can boost prices.
Geopolitical Events: Monitor geopolitical tensions that can disrupt supply chains. Events such as trade wars or conflicts in major oil-producing regions can create volatility in commodity prices.
Currency CFDs
Analyze macroeconomic factors and geopolitical developments that may impact currency values. Interest rate differentials, trade balances, and economic growth rates are crucial in currency analysis.
Interest Rate Differentials: Traders often focus on central bank interest rates and monetary policies. A country with rising interest rates might attract foreign capital, strengthening its currency.
Economic Indicators: Be aware of major economic reports that can impact currency markets. GDP growth, employment figures, and consumer sentiment can cause fluctuations in currency valuations.
Index CFDs
When trading index CFDs, understanding broader market trends and sentiment can provide insights. Monitor economic performance indicators and earnings reports from the companies comprising the index.
Global Market Trends: Global events can influence index performance. Economic downturns in major markets can have ripple effects worldwide.
Sector Weighting: Understand how different sectors contribute to the index. A heavy weighting in technology, for example, may make an index more sensitive to tech earnings reports.

Staying Informed
Continuous Learning
The markets are continually evolving; hence, staying informed is vital. Engage in continuous education through courses, webinars, and reading materials to enhance your understanding of fundamental analysis and CFD trading strategies.
Networking with Other Traders
Join trading communities where you can share insights, discuss strategies, and learn from more experienced traders. Networking can provide valuable perspectives and encourage better trading practices.
Trading Forums: Participating in online trading forums allows you to learn from the experiences and expertise of others in the field.
Local Trading Groups: Consider joining local trading clubs or meetups where you can connect in person with other traders and share strategies.
Utilizing Trading Tools
Many brokers provide advanced trading platforms equipped with analytical tools, charts, and economic calendars. Leverage these tools to conduct thorough analyses and execute trades efficiently.
Charting Software: Powerful charting software helps you visualize price movements and patterns, allowing for better analysis.
Alert Systems: Set up alerts for specific market events or price levels to stay informed about potential trading opportunities without constantly monitoring the market.
Psychological Factors in Trading
The psychology of trading plays a critical role in a trader’s performance. Developing emotional discipline and resilience can differentiate successful traders from those who struggle.
Understanding Emotions: Be mindful of how emotions like fear and greed can influence your trading decisions. Being aware of these tendencies can help you make more rational choices.
Staying Disciplined: Stick to your trading plan and avoid impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements. Consistency is key to long-term success.
Setting Realistic Expectations
Having realistic expectations about potential returns and risks is crucial. Remember that trading involves both winning and losing trades, and it’s essential to manage your expectations accordingly.
Accepting Losses: Losses are a natural part of trading. Learning to accept them without letting them affect your trading psychology is fundamental.
Building Experience: Repeated exposure to the market will help you become a better trader. Focus on the learning process rather than solely on making profits.
Neglecting Risk Management
One of the most significant mistakes traders make is overlooking risk management. Always set stop-loss orders, and never risk more than you can afford to lose.
Overleveraging: Using excessive leverage can lead to significant losses. Use leverage cautiously and in line with your risk tolerance.
Ignoring Diversification: Concentrating too much on a single asset can magnify risk. Diversifying across multiple positions helps mitigate exposure to any one investment.
Relying Solely on Fundamental Analysis
While fundamental analysis is crucial, ignoring technical indicators can lead to misguided trades. A balanced approach is more effective in volatile markets.
Missing Entry/Exit Signals: Fundamental insights might suggest a buy, but technical indicators that signal overbought conditions should not be ignored.
Combining Strategies: Integrate both fundamental and technical analysis for a comprehensive approach to decision-making.
Overreacting to Market News
Traders often react impulsively to breaking news, leading to poor decision-making. Take a measured approach and analyze the broader implications before acting on news events.
Immediate Reactions: Avoid making hasty decisions based solely on headlines. Take the time to analyze how news may affect underlying fundamentals.
Developing a Plan: Create a plan for responding to news—a checklist that includes economic indicators, market sentiment, and analysis before executing trades.
Lack of a Trading Plan
Trading without a structured plan often leads to confusion and emotional trading. Always have a clear strategy outlining your goals, entry/exit points, and risk management measures.
Setting Guidelines: Write down your trading strategy, including rules for entering and exiting trades, and stick to it.
Reviewing Your Plan: Regularly review and adjust your trading plan based on performance and changing market conditions.
Emerging Trends in CFD Trading
As technology evolves, so too does CFD trading. Traders are witnessing shifts in market dynamics and technological advancements that could shape the future of CFD markets.
Algorithmic Trading: Increased use of algorithms and automated trading systems can help traders execute trades more efficiently and capitalize on rapid market movements.
Increased Regulation: As CFD trading grows in popularity, regulators are paying closer attention. Understanding emerging regulations is crucial for traders to remain compliant.
Adoption of Blockchain Technology: Blockchain has the potential to enhance transparency and security in trading processes, which could positively impact CFD trading in the future.
The Impact of Global Economic Changes
The global economy continually evolves, impacting all areas of trading. For CFD traders, being attuned to these changes is crucial for adapting strategies and remaining competitive.
Globalization: The interconnectedness of markets means that developments in one region can ripple across the globe, affecting asset prices dramatically.
Emerging Markets: As emerging markets grow, so do trading opportunities in these areas. Understanding the unique factors that drive prices in these markets can open new avenues for traders.
Fundamental analysis is a vital component of successful CFD trading. By understanding the economic landscape and applying fundamental principles, traders can make informed decisions that enhance their trading strategies. While CFD trading presents opportunities for profit, it also comes with inherent risks—hence the importance of continuous learning, effective risk management, and a balanced approach to analysis. With dedication and the right tools, beginners can navigate the world of CFDs and establish a successful trading career.
Incorporating fundamental analysis into your trading strategy not only allows you to perceive the market from a macroeconomic perspective but also equips you with insights necessary to make data-driven decisions. As you continue your journey in CFD trading, embrace both the analytical methods and the psychological aspects of trading to ultimately enhance your trading outcomes.
Looking to trade CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.