
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Friday Nov 21 2025 07:45

17 min

CFD Trading Explained: Contracts for Difference (CFDs) have become a popular financial instrument for traders seeking to benefit from price movements in a wide range of markets.
CFD trading basics: This article provides an in-depth exploration of CFD trading, covering its fundamental principles, operational mechanics, advantages, risks, and key considerations for anyone interested in this form of trading.
CFD trading involves entering into a contract between two parties — typically described as the buyer and the seller — to exchange the difference in the value of an underlying asset from the time the contract is opened to when it is closed. Unlike traditional trading, where ownership of the physical asset is transferred, CFD trading allows traders to speculate on price movements without owning the asset itself.
CFDs are popular across various asset classes including stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, and cryptocurrencies. They offer a flexible way to gain exposure to markets without the need for significant capital outlay.
When trading CFDs, the trader agrees to exchange the difference in price of an asset between the opening and closing of the contract. If the price moves in the trader’s favor, they receive the difference. Conversely, if the price moves against the trader, they owe the difference.
Opening a Position
To open a position, a trader selects an asset and specifies whether they want to go long (buy) or short (sell). Going long means expecting the price to rise, while going short means anticipating a decline in price. The trader then decides on the size of the position, which is often measured in contracts or units.
Closing a Position
The position is closed by executing the opposite trade to the one that opened it. The profit or loss is the difference between the opening and closing prices, multiplied by the position size.
Margins and Leverage
One of the defining features of CFD trading is the use of margin. Margin is a deposit that allows traders to open positions larger than the amount of capital they have available. This is achieved through leverage, which magnifies both gains and losses.
For example, a trader might only need to deposit a fraction of the total trade value to open a position. While this can increase potential returns, it also increases exposure to risk, as losses can exceed the initial margin deposit.

CFD trading offers several advantages to traders, which have contributed to its widespread popularity.
Access to a Wide Range of Markets
CFDs provide access to a broad spectrum of markets from a single trading platform. Whether interested in stocks, commodities, indices, forex, or cryptocurrencies, traders can diversify their portfolios without the need to open multiple accounts or navigate different exchanges.
Ability to Trade Both Up and Down Markets
Unlike traditional investing, which typically involves buying assets in anticipation of price appreciation, CFD trading allows speculation on both rising and falling markets. Traders can open long positions to benefit from price increases and short positions to profit from declines.
Leverage Enhances Capital Efficiency
Leverage enables traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This enhances capital efficiency and can amplify returns. However, it is essential to understand that leverage also increases risk exposure.
No Ownership of the Underlying Asset Required
Since CFDs are derivative products, traders do not take physical ownership of the underlying asset. This reduces barriers such as settlement delays, custody fees, or dealing with complex regulations related to asset ownership.
Flexible Trade Sizes
CFDs allow for flexible trade sizes, enabling traders to start with small positions and scale up as they gain experience or confidence. This flexibility suits both beginners and seasoned traders.
Fast Execution and Liquidity
CFD platforms typically offer fast trade execution and high liquidity, allowing traders to enter and exit positions quickly. This is particularly beneficial for short-term trading strategies such as day trading or scalping.
Hedging Capabilities
CFDs can be used to hedge existing portfolios. For instance, if a trader holds physical shares, they can open a short CFD position on the same stock to offset potential losses during market downturns.
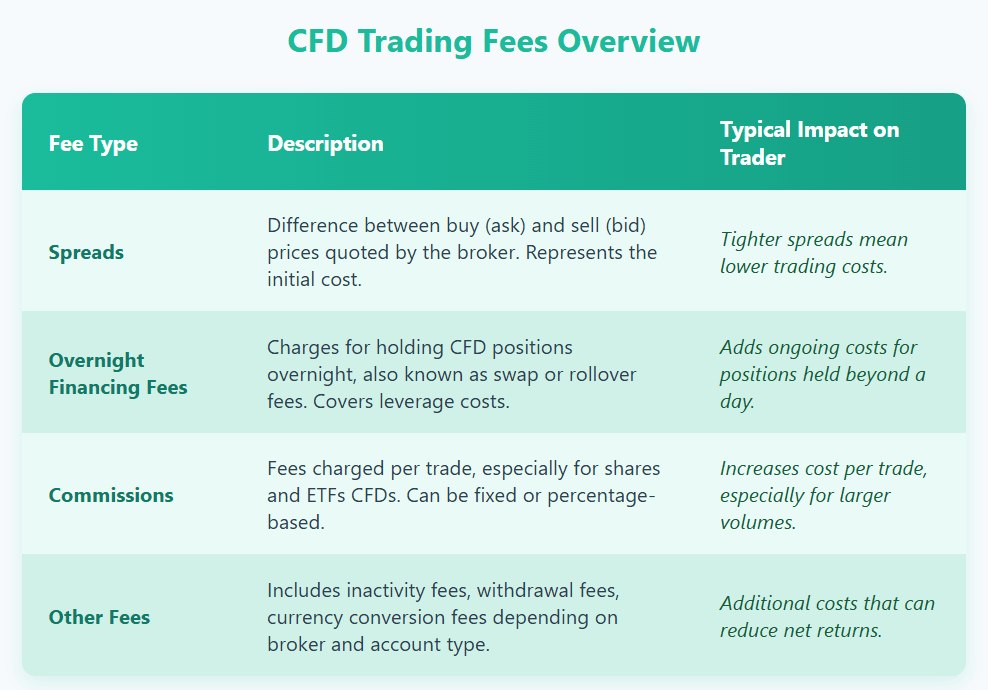
While there are many benefits, CFD trading also involves costs that traders need to be aware of.
Spreads
The spread is the difference between the buy (ask) and sell (bid) prices quoted by the broker. This is effectively a cost to the trader, as they start a trade at a slight disadvantage. Tighter spreads generally indicate better pricing and lower costs.
Overnight Financing Fees
Most CFD positions held overnight incur financing costs, often referred to as swap or rollover fees. This fee compensates the broker for the leverage provided and varies depending on the asset and market interest rates.
Commissions
Some CFD brokers charge commissions on trades, particularly for shares and ETFs. These commissions are either fixed or variable and should be factored into the overall cost of trading.
Other Fees
Additional costs such as inactivity fees, withdrawal fees, or currency conversion fees may apply depending on the broker and account type.
CFD trading carries risks that must be fully understood before engaging in this market.
Market Risk
The most obvious risk is the market moving against the trader’s position, leading to losses. Because CFDs allow for leveraged trading, losses can exceed the initial investment.
Leverage Risk
Leverage amplifies outcomes in both directions. While it can magnify gains, it can also accelerate losses. This makes proper risk management essential.
Counterparty Risk
Since CFDs are over-the-counter products, traders are exposed to the credit risk of the broker. Choosing a reputable, regulated broker helps reduce this risk.
Liquidity Risk
In certain market conditions, liquidity might dry up, making it harder to close positions at desired prices. This can cause slippage or wider spreads.
Regulatory Risk
CFD trading is regulated differently across jurisdictions. Changes in regulations may affect availability, leverage limits, or trading conditions.
Effective risk management is critical for longevity and success in CFD trading.
Use of Stop-Loss Orders
Placing stop-loss orders automatically closes a position at a predetermined price level, limiting potential losses.
Position Sizing
Determining the appropriate size of each trade relative to the overall portfolio helps prevent excessive exposure.
Leverage Control
Using lower leverage reduces the risk of large losses and allows for more sustainable trading.
Diversification
Spreading trades across multiple assets or markets can reduce the impact of adverse moves in any single position.
Regular Monitoring
Active monitoring of open positions and market conditions allows timely adjustments and risk mitigation.
Various strategies can be applied to CFD trading depending on the trader’s style and goals.
Day Trading
Day traders open and close positions within the same day, aiming to profit from short-term price fluctuations.
Swing Trading
Swing traders hold positions for several days to capture medium-term trends.
Scalping
Scalpers make numerous trades throughout the day for small profits on each trade.
Trend Following
This strategy involves identifying and trading in the direction of prevailing market trends.
Hedging
Using CFDs to offset risk exposure in other investments.

1. IG
Overview:
IG is one of the oldest and most reputable CFD brokers globally, with a strong regulatory presence in multiple jurisdictions. It offers a comprehensive suite of markets and trading tools suitable for both beginners and professional traders.
Key Features:
Why Choose IG:
IG’s global reputation, advanced tools, and broad asset coverage make it ideal for traders seeking reliability and variety.
2. Pepperstone
Overview:
Pepperstone is a well-regarded Australian broker known for low spreads and fast execution, focusing heavily on forex and CFD trading.
Key Features:
Ideal for active and algorithmic traders who prioritize low-cost execution and fast trade processing.
3. Mitrade
Overview:
Mitrade is a newer entrant with a focus on simplicity and mobile-first trading, making it appealing for beginners and casual traders.
Key Features:
Why Choose Mitrade:
Great for those who want a straightforward, hassle-free trading experience with built-in risk controls.
4. XTB
Overview:
XTB is a European broker with a strong presence worldwide, offering a versatile trading experience with a focus on technology and education.
Key Features:
Why Choose XTB:
Perfect for traders looking for a balanced offering of advanced tools and educational support, especially in Europe.
5. Markets.com
Overview:
Markets.com offers a user-friendly trading environment with a diverse range of assets and innovative trading tools.
Key Features:
Market Access: Hundreds of CFDs including stocks, forex, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and ETFs.
Why Choose Markets.com:
Well-suited for traders who want a cutting-edge platform with AI tools and broad market coverage.
Markets.com is a well-known online trading platform that offers access to a wide range of financial markets, including Contracts for Difference (CFDs) on stocks, indices, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies. If you’re interested in starting CFD trading with Markets.com, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the essential steps to get started.
Step 1: Register an Account
The first step is to create an account on Markets.com.
Markets.com follows strict regulatory requirements, so you’ll need to verify your identity and address by uploading documents such as a government-issued ID (passport or driver’s license) and a recent utility bill or bank statement.
Step 2: Fund Your Trading Account
Before you can start trading CFDs, you need to deposit funds into your Markets.com account.
Markets.com supports multiple currencies and provides a secure payment process. Beginners are advised to start with a small deposit to familiarize themselves with the platform and CFD trading.
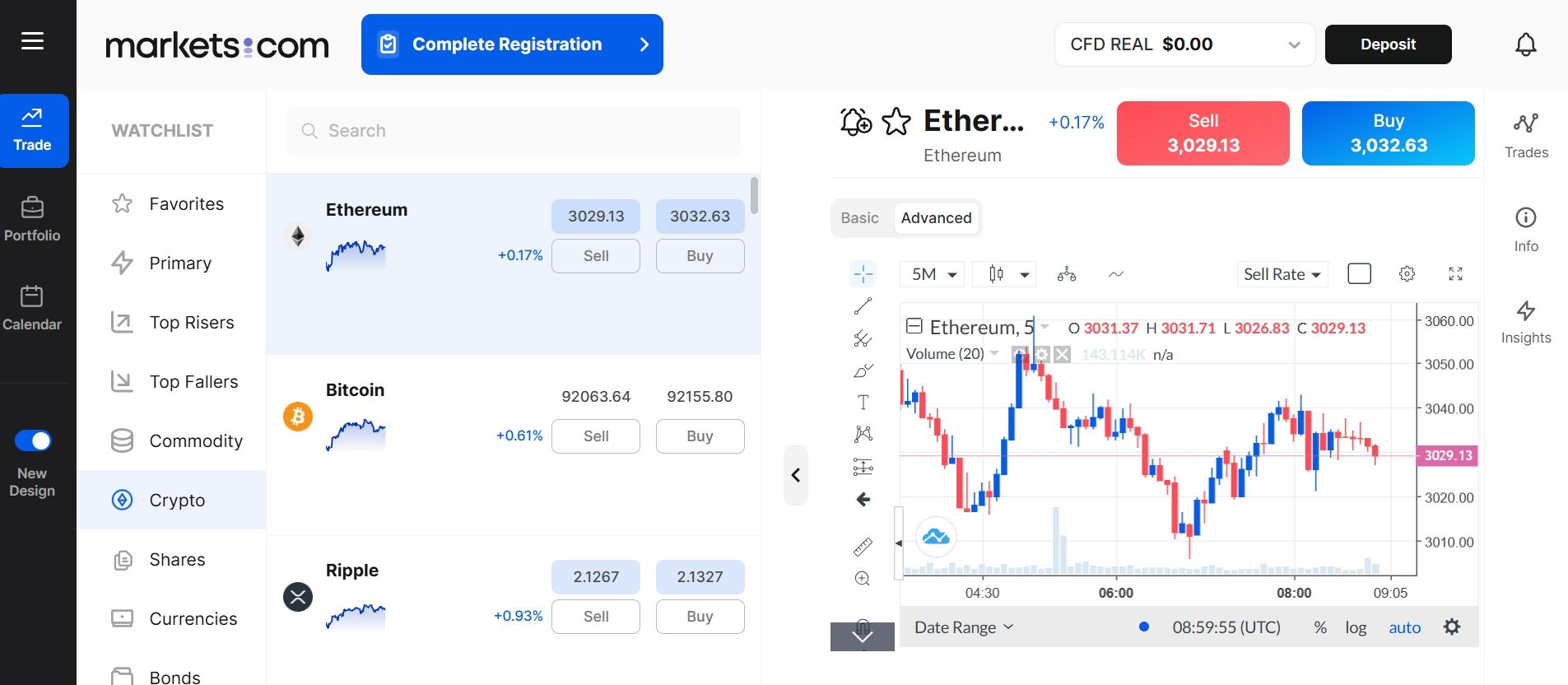
Step 3: Explore the Trading Platform
Markets.com offers both a web-based platform and a mobile app, both designed with user-friendly interfaces.
You can also open a demo account before risking real money. This allows you to practice trading CFDs with virtual funds and explore the platform’s features without financial risk.
Step 4: Choose Your CFD to Trade
Once familiar with the platform, it’s time to select the asset you want to trade.
Step 5: Place Your CFD Trade
After choosing an asset:
Your trade will then appear in your portfolio where you can monitor its performance in real-time.
Step 6: Monitor and Manage Your Trades
Active management of your open positions is crucial in CFD trading.
Additional Tips
Starting CFD trading with Markets.com is straightforward. By registering an account, funding it, selecting assets, and placing trades, you can participate in global financial markets with flexibility and leverage. Remember that while CFDs offer great opportunities, they also carry risks, so take time to learn and trade responsibly.
CFD trading is a versatile and powerful financial tool that offers access to global markets with flexibility and leverage. Its ability to allow speculation on price movements without owning the underlying asset makes it attractive to a wide range of traders.
However, CFDs carry risks that require careful consideration, understanding, and disciplined risk management. Choosing a regulated broker, educating oneself thoroughly, and employing well-planned strategies are key steps toward navigating CFD trading successfully.
With the right approach, CFD trading can be an effective way to participate in financial markets and pursue trading goals across diverse asset classes.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.