
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Tuesday Nov 4 2025 09:52

7 min

Impact of the Fed's Interest Rate: The Federal Reserve's decisions on interest rates are among the most closely watched economic events worldwide.
Both increases and cuts in the Fed Funds Rate shape economic activity, influence asset prices, and affect market sentiment. Understanding the effects of these changes, especially rate cuts, provides insight into how markets respond and how participants might adjust.
Throughout history, the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates to manage inflationary pressures and prevent the economy from overheating. These cycles typically begin when economic growth is strong, and inflation threatens to accelerate beyond desired levels. By increasing the cost of borrowing, the Fed aims to cool demand in the economy, slowing price increases and maintaining balance.
During rate hike cycles, borrowing becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers alike. This usually leads to reduced spending on investments, homes, and consumer goods. The effects ripple through financial markets: stock prices may face downward pressure as future earnings growth is discounted at higher rates, and bond prices adjust accordingly. Additionally, sectors dependent on cheap credit, such as real estate and utilities, often react negatively.
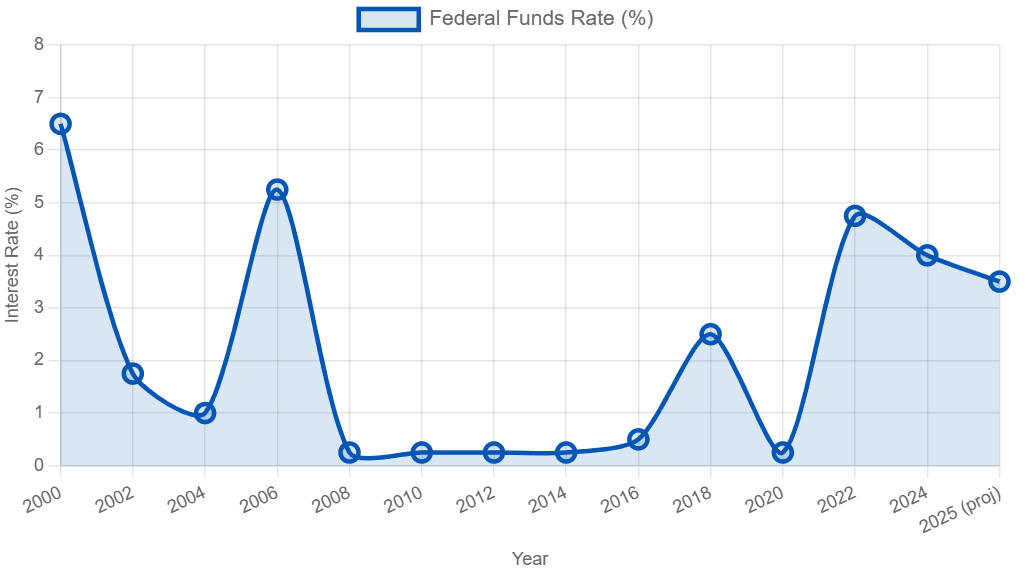
Markets usually anticipate these moves, and volatility tends to increase as participants digest the pace and scale of hikes. These tightening cycles have historically been followed by periods of economic slowdown or recession, underscoring the balancing act the Fed must perform.
Looking ahead to 2025, the direction of the Federal Reserve's interest rate policy will largely depend on economic indicators such as inflation trends, employment levels, and global economic conditions. If inflation pressures ease, there may be room for the Fed to reduce rates, aiming to encourage borrowing, spending, and investment.
A rate cut in this environment typically signals a shift toward stimulating economic activity, which can encourage risk-taking and support broader market growth. Conversely, if inflation remains elevated or economic conditions deteriorate, the Fed might maintain or even increase rates to preserve price stability.
Global economic developments and geopolitical factors will also influence the Fed’s stance. Coordination or divergence with other central banks’ policies can impact currency markets and cross-border capital flows.
Between 2022 and 2025, the Federal Reserve grappled with balancing inflation control and supporting the economy. Initially, the Fed implemented a series of rate increases to address rising inflation, which affected borrowing costs and liquidity conditions.
These rate hikes brought about adjustments in consumer and corporate behavior, influencing spending and investment decisions. The tightening of monetary policy also created shifts in market sentiment, with increased caution towards riskier assets.
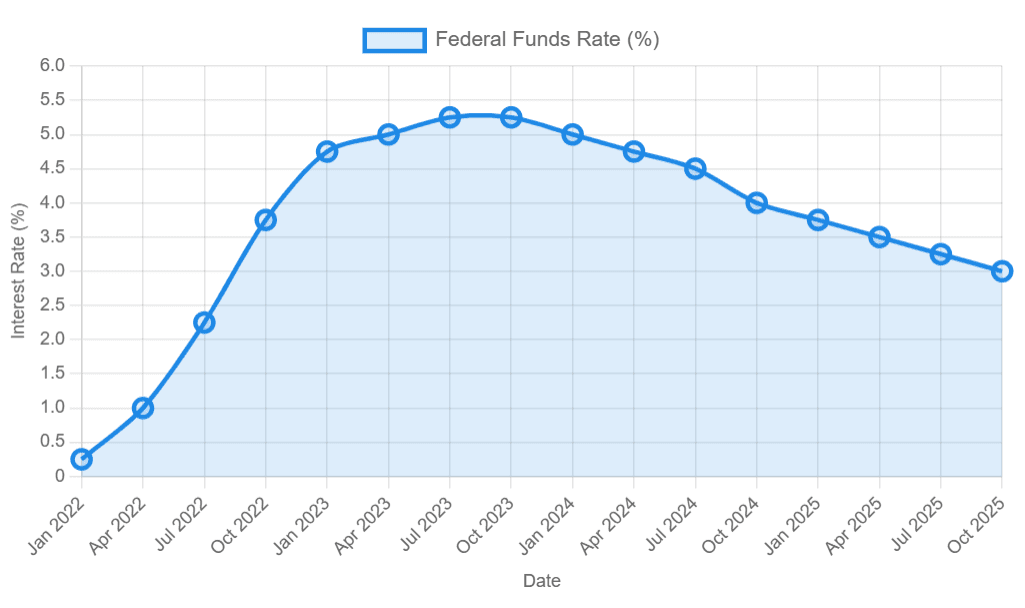
Later, as inflation pressures began to moderate, the Fed’s focus shifted toward assessing economic resilience and finding a balance between curbing inflation and avoiding undue economic slowdown. The decisions during this period reflected a careful calibration of policy, with pauses and adjustments signaling responsiveness to evolving data.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency markets tend to be sensitive to changes in interest rates due to their speculative nature and reliance on liquidity. When rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, often reducing speculative capital available for crypto trading. Additionally, higher rates can increase the attractiveness of traditional interest-bearing assets, drawing capital away from digital currencies.
Conversely, rate cuts generally encourage more risk-taking and can lead to increased demand for cryptocurrencies. However, the volatility of crypto assets means reactions can be swift and pronounced, sometimes disconnected from traditional market dynamics.
Gold (XAU/USD)
Gold prices usually respond to the interplay between interest rates and inflation expectations. Rising interest rates increase the appeal of yield-bearing assets, which can reduce demand for gold, a non-yielding asset. Additionally, higher rates often strengthen the currency in which gold is priced, exerting downward pressure on gold prices.
When rates are cut, gold can benefit as the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets decreases. Inflation expectations also weigh heavily, as gold is often viewed as a store of value during periods of rising prices.
Stock Market
Higher interest rates tend to increase the cost of capital for companies, which can dampen earnings growth expectations and put downward pressure on stock valuations. Sectors reliant on debt financing or sensitive consumer spending often face headwinds during rate hikes.
Financial sectors, however, may experience improved margins as rates rise. Overall, rate hikes often lead to rotation between sectors and increased volatility as market participants reassess risk and return profiles.
When rates are lowered, stocks generally benefit from cheaper borrowing costs and improved consumer spending power, which can support earnings momentum.
Forex Market
Interest rate changes have a direct impact on currency values through yield differentials and capital flows. A rate hike by the Fed tends to strengthen the U.S. dollar as higher yields attract foreign funds. This appreciation influences trade dynamics and multinational corporate earnings.
Rate cuts can weaken the dollar, potentially boosting exports but increasing import costs. Currency markets are highly responsive to Fed policy shifts, with traders often positioning themselves in anticipation of changes.

Market participants should approach Fed interest rate decisions with a well-informed and measured mindset. Here are some considerations for navigating these changes:
Diversification: Spreading exposure across asset classes can reduce the impact of adverse moves in any single market segment.
Adjusting Duration in Fixed Income: Shortening bond durations may help manage sensitivity to rising rates, while longer durations can benefit from falling rates.
Sector Rotation: Aligning sector exposure with the interest rate environment can help maintain portfolio balance, favoring defensive sectors during hikes and cyclical sectors during cuts.
Currency Risk Management: For those with international exposure, monitoring currency movements and hedging when necessary can mitigate exchange rate impacts.
Stay Informed: Following economic data releases and Fed communications helps anticipate policy moves and market reactions.
Risk Management: Using appropriate tools and position sizing can help weather periods of increased volatility around Fed decisions.
Maintain a Long-Term Perspective: Interest rate cycles are part of broader economic trends. Keeping a long-term view helps avoid overreacting to short-term market fluctuations.
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate adjustments have far-reaching consequences across financial markets. Rate hikes generally lead to tighter financial conditions, affecting borrowing costs, asset valuations, and market sentiment, while rate cuts aim to stimulate growth and liquidity.
Different markets—cryptocurrencies, gold, stocks, and forex—respond uniquely depending on their characteristics and sensitivities. Being mindful of these distinctions and adopting a thoughtful approach to portfolio management can help participants navigate the complexities of monetary policy shifts.
By understanding the historical context and anticipating future trends, participants can make more informed decisions amid an evolving economic landscape shaped by the Fed’s interest rate policies.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.