
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Wednesday Jan 14 2026 09:13

16 min

What is FTSE 100 Index: The FTSE 100 Index, commonly referred to as the FTSE, represents the largest 100 companies listed on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) based on market capitalization.
UK stock market analysis: It serves as a vital indicator of the economic health of the UK and is widely followed by investors globally. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the FTSE 100 Index, its significance in the financial markets, and how to trade FTSE 100 Index Contracts for Difference (CFDs) using Markets.com.
Overview of the FTSE 100
Launched in 1984, the FTSE 100 Index has grown to become one of the most recognized stock indices globally. It reflects the economic strength and diversity of the UK market, encompassing companies across various sectors, including finance, technology, consumer goods, and healthcare. The companies in the index are subject to rigorous criteria, ensuring that only the most reliable and influential firms are represented.
Importance of the FTSE 100
Understanding the FTSE 100 is crucial for investors, analysts, and policymakers alike. Its significance lies in:
Economic Indicator: The FTSE 100 serves as a barometer for the UK economy. Rising values often correlate with economic growth, while declines may signal looming issues like recession or market correction.
Investment Benchmark: The index is widely used as a benchmark against which mutual funds, ETFs, and other investment portfolios are measured, making it a point of reference for performance assessments.
Global Influence: The international presence of FTSE 100 companies means that the index can also be affected by global events, making it relevant to investors outside the UK.
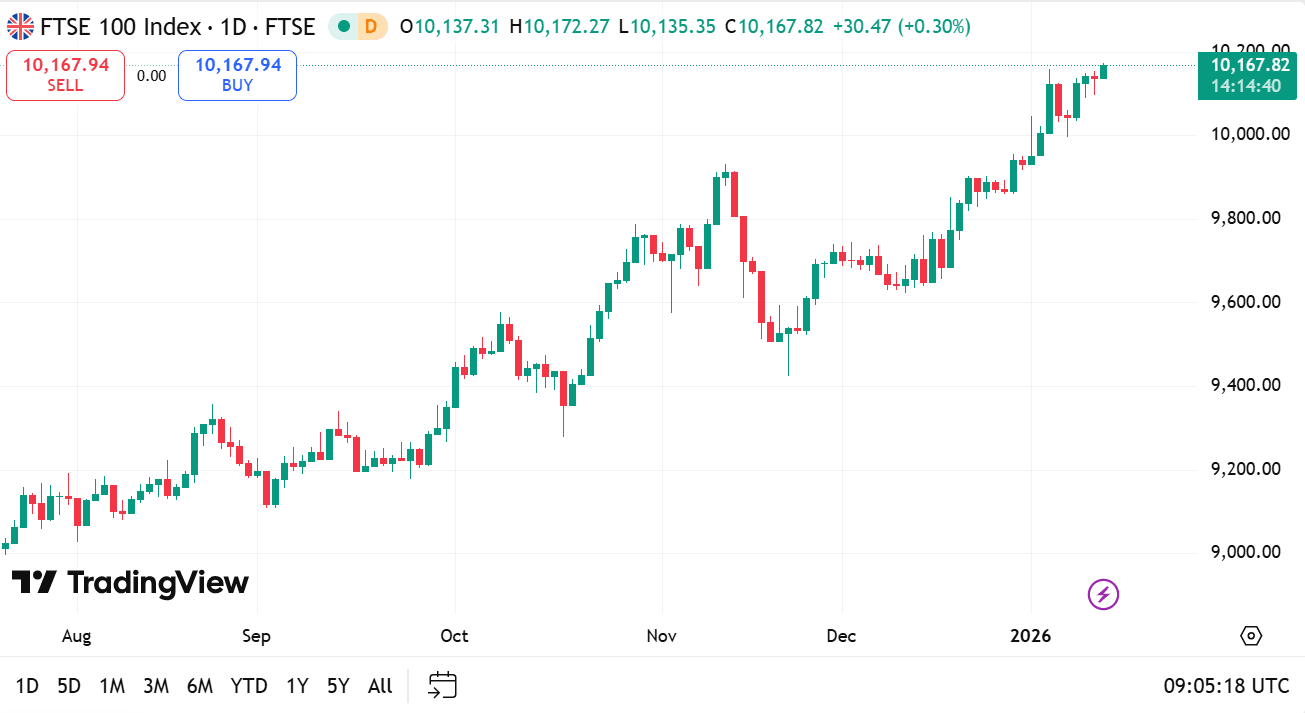
source: tradingview
Leading Companies in the Index
The FTSE 100 features several globally recognized corporations. Some of the key constituents include:
BP Plc: A major player in the energy sector, BP is involved in the exploration and production of oil and gas, as well as renewable energy initiatives.
HSBC Holdings: As one of the world's largest banking and financial services organizations, HSBC has a significant influence on the UK and global markets.
Unilever: This multinational consumer goods company is known for its diverse portfolio, which includes food, beverages, cleaning agents, beauty products, and health and well-being items.
These prominent companies not only contribute to the index's overall performance but also serve as indicators of their respective sectors' health.
Sector Allocation
The sector allocation within the FTSE 100 is diverse and reflects the broader economy:
Financials (≈ 23%): This sector includes banks, insurance companies, and asset management firms. The performance of financial stocks can heavily influence the overall index.
Energy (≈ 10%): Comprising major oil and gas companies, the energy sector's performance is often linked to global oil prices and geopolitical events.
Consumer Staples (≈ 18%): Companies that provide essential goods tend to maintain stable performance, even during economic downturns, providing a cushion to the index.
Healthcare (≈ 13%): Pharmaceutical and healthcare firms are integral to the index as they are often less volatile and resilient during market fluctuations.

What are CFDs?
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) allow traders to speculate on the price movements of an asset without actually owning it. When you trade FTSE 100 CFDs, you are essentially betting on whether the index will rise or fall.
Benefits of Trading CFDs
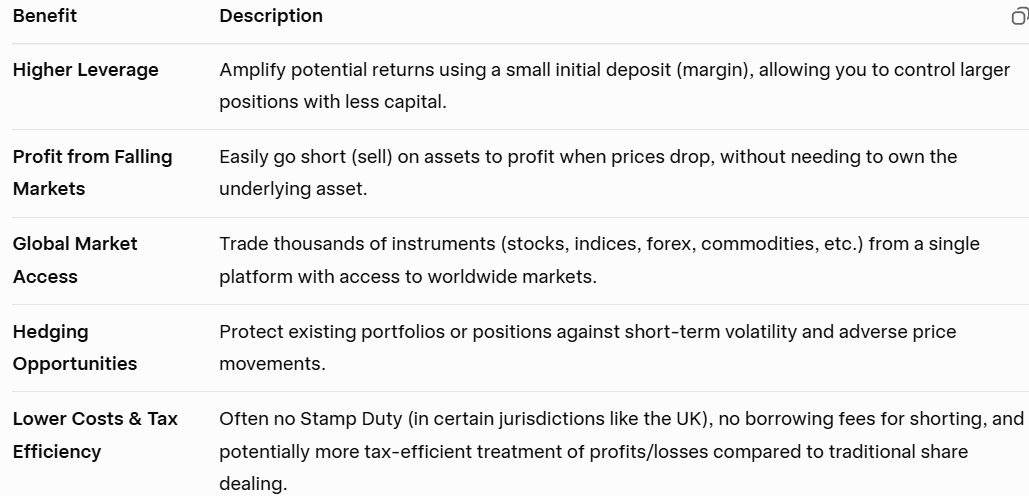
Leverage: CFDs offer the ability to control larger positions with a small amount of capital, effectively amplifying both potential gains and losses.
Short Selling: Unlike traditional stock trading, CFDs allow you to profit from price declines. You can sell a CFD when you believe the FTSE 100 will decrease, potentially leading to significant gains if your prediction is correct.
No Ownership: Since you do not own the underlying assets, there are no additional costs associated with buying and holding stocks, such as dividend payments or ownership documentation.
Variety: CFDs can often be traded on various underlying assets, including indices, stocks, commodities, and currencies, providing the investor a diverse trading environment.
Setting Up an Account
To trade FTSE 100 Index CFDs on Markets.com, follow these steps:
Registration: Create an account on Markets.com by providing your necessary personal and financial information.
Verification: Depending on local regulations, you may need to undergo a verification process to confirm your identity and age.
Funding Your Account: Markets.com provides various funding options, including credit/debit cards, bank transfers, and e-wallet solutions, allowing you to deposit funds easily.
Choosing an Account Type: Markets.com offers different account types tailored to varying trading needs, so consider your trading style and choose accordingly.
Platform Overview
Markets.com provides an intuitive trading platform equipped with a variety of tools and features:
Advanced Charts: Access real-time price charts, allowing you to analyze trends and patterns with technical indicators.
Research Tools: Utilize market analysis, economic calendars, and news updates to stay informed about events that may affect the FTSE 100 Index.
Mobile Trading: With a mobile app, you can trade on the go, ensuring you never miss out on market movements.
Customer Support: Markets.com offers responsive customer service to assist you with any inquiries regarding your trading experience.
Fundamental Analysis
A comprehensive analysis of the FTSE 100 goes beyond mere price charts. Investors should consider key economic indicators and geopolitical factors:
Economic Data: Monitor UK economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment statistics, as they significantly impact investor confidence and market sentiment.
Interest Rates: Decisions made by the Bank of England regarding interest rates can have a substantial effect on the index. Lower rates typically stimulate spending and investment, leading to higher equity prices, while higher rates can have the opposite effect.
Political Stability: The stability of the UK government, along with its fiscal policies, affects market sentiment. Events such as elections or major policy changes can lead to market volatility.
Global Events: Trade agreements, tariffs, and geopolitical tensions can influence the performance of FTSE 100 companies, especially those operating on a global scale.

Technical Analysis
In addition to fundamental analysis, traders often use technical analysis to make informed trading decisions. Key components of technical analysis include:
Support and Resistance Levels: Identifying key price levels at which the FTSE 100 has historically reversed direction can help traders set entry and exit points.
Candlestick Patterns: Understanding different candlestick formations, such as dojis or hammers, can provide insight into potential market reversals.
Technical Indicators: Utilize tools such as Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) to identify trends, momentum, and potential buy/sell signals.
Volume Analysis: Monitoring trading volume can help validate price movements; a price increase accompanied by high volume may suggest a strong trend.

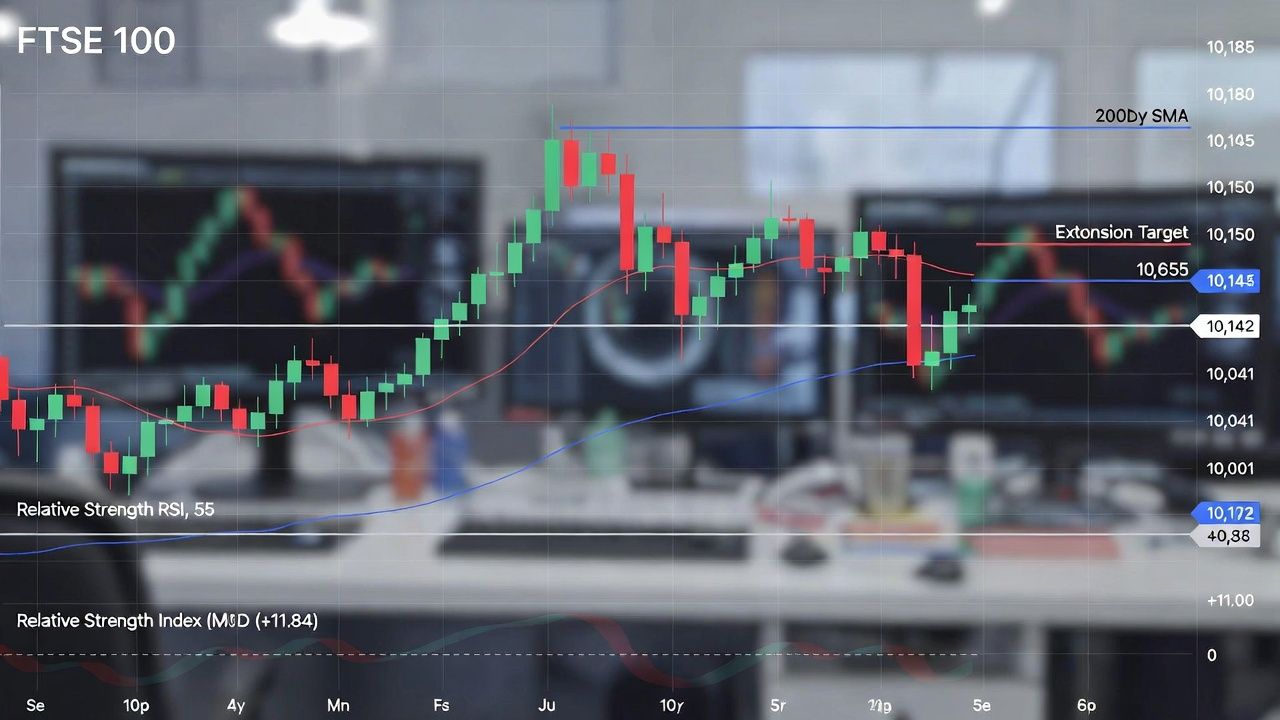
The index benefited from global commodity/inflation plays, Bank of England rate cuts, share buybacks, and its multinational exposure (75%+ revenues overseas), insulating it from UK domestic weakness.
Entering 2026 (as of mid-January), the FTSE 100 has already broken the symbolic 10,000 milestone for the first time intraday and on closes in early January (e.g., hitting ~10,046 shortly after New Year, with levels around 10,054–10,142 recently amid some pullbacks from oil/miner softness).
Analysts and models are generally positive but expect more moderate gains than 2025's surge, with choppiness from global volatility, policy shifts, and commodity swings:
Consensus drivers: Continued BoE easing (supporting rate-sensitive sectors like banks/utilities), resilient earnings (~14% profit growth forecast), dividend growth (~6%, potentially record payouts ~£85–86bn), and buybacks. The index trades at a P/E discount (~14x) vs. global peers, seen as undervalued.

AJ Bell: Potential fresh highs, supported by earnings/dividends (implying upside to ~10,750+).
UBS/other strategists: Around 10,800 as a plausible target.
Statistical/long-term models: End-2026 averages ~11,300–11,600 (e.g., Traders Union ~11,597; some higher to 11,800+), with ranges 11,365–11,829.
Optimistic extensions: 12,000+ by late 2026 if momentum holds (e.g., some forecasts see 12,445 early Nov).
More cautious views: Sideways or mild pullback risk if recession/oil surplus hits cyclicals (some models ~9,100–10,000 range).
Key risks: Global slowdown, commodity reversals (oil/miners heavy weighting), geopolitical events, or delayed rate cuts.
Overall sentiment: Bullish continuation likely in a "mild Goldilocks" environment (modest growth + easing policy), with 10,000+ sustained and potential for 5–15% upside to 10,750–11,600 by year-end, though volatility expected.
Day Trading
Day trading is a short-term strategy where traders look to capitalize on small price movements within a single trading day. Day traders typically close all positions before the market closes to avoid overnight risks.
Tips for Day Trading the FTSE 100:
Swing Trading
Swing trading is a medium-term strategy that seeks to capture price swings over days to weeks. Swing traders often leverage technical analysis to identify good entry and exit points based on market trends.
Tips for Swing Trading the FTSE 100:
Hedging Strategies
Hedging is a risk management strategy employed by traders to offset potential losses in one position with gains in another. When trading FTSE 100 CFDs, hedging can protect against market volatility.

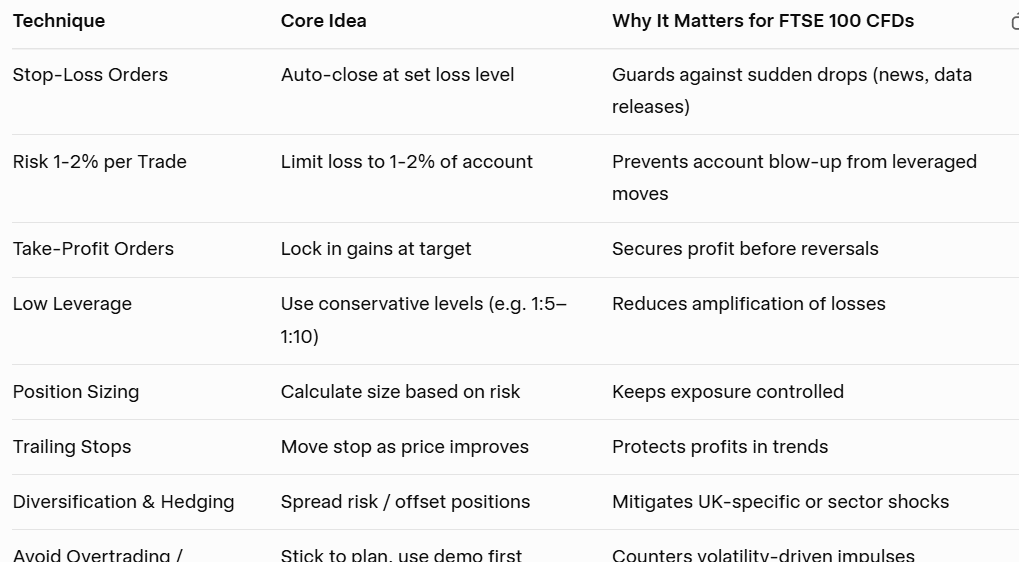
Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
Effective risk management is crucial when trading CFDs. Setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels helps limit your losses and secure profits.
Stop Loss: Identify a maximum loss that you are willing to accept. Place a stop-loss order slightly below the support level for long trades and above the resistance level for short trades.
Take Profit: Set a take-profit order at a predefined level where you want to secure your gains. A common strategy is to use a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2—meaning for every unit of risk, you aim for two units of reward.
Diversification
Putting all your capital into a single trade can expose you to significant risks. Diversifying your investments helps control risk:
Asset Diversification: Invest across different asset classes (stocks, commodities, currencies) to cushion against adverse market conditions.
Sector Diversification: Within the FTSE 100, consider spreading your investments across various sectors. This approach helps mitigate risks posed by sector-specific downturns.
Tax Implications of Trading CFDs
Trading CFDs can have tax implications depending on local regulations. It's essential to understand the tax responsibilities associated with your trading activities:
Consulting with a tax professional can ensure that you’re compliant and optimized for tax implications arising from your trading activities.

Psychological Factors in Trading
Trading isn't solely about analysis and strategy; psychology plays a crucial role as well. Emotional decision-making can lead to significant losses. Understanding common psychological pitfalls can help:
Common Psychological Pitfalls
Fear and Greed: These emotions can lead to impulsive decisions—fear may lead you to exit trades too early, whereas greed might encourage you to hold onto losing positions longer than advisable.
Overconfidence: As you gain experience, it’s easy to fall into the trap of overconfidence, which can lead to reckless trading decisions.
Loss Aversion: Traders often prefer avoiding losses over acquiring gains, which can lead to adverse trading behaviors.
Developing a Trading Discipline
Set a Trading Plan: Establish a comprehensive trading plan that includes entry and exit strategies, risk management rules, and goal-setting.
Stick to the Plan: Avoid deviating from your plan in response to market volatility. Discipline is vital for consistent trading success.
Keep a Trading Journal: Maintaining a trading journal aids in self-reflection, helping identify flaws in your trading plan and emotional responses.
The FTSE 100 Index is a vital component of the global financial landscape, and trading its CFDs offers numerous opportunities for investors. By understanding the dynamics of the index, employing effective trading strategies, and utilizing robust risk management practices, traders can enhance their confidence and performance in the market.
Markets.com stands out as a reliable platform, offering a suite of tools aimed at both novice and experienced traders. From research resources to advanced trading features, Markets.com is committed to supporting your trading journey.
As you venture into trading FTSE 100 Index CFDs, remember that thorough research, strategic planning, and disciplined execution are keys to achieving your investment goals. Furthermore, staying abreast of economic and geopolitical developments can significantly affect your trading results.
Looking to trade FTSE 100 Index CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.