
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Monday Jan 12 2026 09:01

16 min

What is the Russell 2000: The Russell 2000 Index is an essential benchmark for measuring the performance of small-cap companies in the United States.
Starting Index trading: As a prominent index, it offers investors insights into the health of the smaller segment of the U.S. economy, which can differ significantly from the performance of large-cap indices. This article will provide an in-depth exploration of the Russell 2000 Index, its components, how it works, and steps to trade or invest in it, emphasizing markets.com as a bridge for potential investors in this dynamic space.
The Russell 2000 Index is a stock market index that measures the performance of 2,000 small-cap companies in the U.S. equity market. It is a subset of the Russell 3000 Index, which includes the 3,000 largest U.S. companies based on total market capitalization. The Russell 2000 was created by the Frank Russell Company in 1984 and has become a critical benchmark for small-cap stocks.
The Russell 2000 Index is a key benchmark in the U.S. stock market, tracking the performance of approximately 2,000 small-cap companies (typically with market caps under $2-10 billion). As a subset of the broader Russell 3000, it represents the small-cap segment and offers unique insights distinct from large-cap-focused indexes like the S&P 500.
The Russell 2000 Index is a widely followed benchmark that measures the performance of the small-cap segment of the U.S. equity market. Maintained by FTSE Russell (a subsidiary of the London Stock Exchange Group), it serves as a subset of the broader Russell 3000 Index, which covers approximately 98% of the investable U.S. equity universe. The Russell 2000 includes roughly 2,000 of the smallest companies from that universe, providing an unbiased, comprehensive view of small-cap stocks.
Industry Composition
The Russell 2000 consists of companies from various sectors. The most significant industries within the index include:
Healthcare
This sector holds substantial weight (~16.7%) in the Russell 2000, featuring biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and medical equipment firms. Small-cap healthcare companies drive innovation through drug pipelines, biotech advancements, and specialized devices, often in early development stages. This leads to high volatility from trial outcomes, regulatory approvals, and funding rounds, but offers strong growth potential amid aging demographics and medical progress. More U.S.-focused than large-cap peers, these stocks react to domestic policies and reimbursement trends. Recent biotech momentum has boosted sector performance, making it a key contributor to small-cap upside in innovative environments.
Information Technology
Small tech firms comprise a notable portion (~13.4%), including software, cybersecurity, cloud services, and emerging innovators. These companies fuel digital transformation, AI adoption, and niche disruptions, providing entrepreneurial exposure beyond mega-caps. Small-cap tech shows higher sensitivity to interest rates and risk sentiment, thriving in low-rate, growth-friendly conditions while facing volatility from tech cycles and competition. It captures underrepresented innovation, with many future leaders emerging here. In early 2026, the sector benefits from broadening AI trends, supporting small-cap rotation and diversification.
Consumer Discretionary
This sector (~12.9%) includes retail, leisure, apparel, and consumer services, showing strong volatility tied to consumer confidence and spending. Small-cap discretionary businesses are highly domestic, reacting to employment, income trends, and economic cycles—booming in expansions but weakening during slowdowns or inflation. Unlike global large-caps, they capture niche retail concepts and entrepreneurial trends. Lower rates and improving sentiment in 2026 position the sector for gains during recoveries, as consumers increase discretionary purchases. It adds cyclical leverage to small-cap portfolios.
Financials
The largest sector (~18.2%), dominated by regional banks, community lenders, insurance, and financial services. These firms serve as economic proxies, sensitive to interest rates, lending volumes, credit conditions, and regulations. Lower rates improve margins and borrowing activity, while growth supports loan demand. Small-cap financials reflect U.S.-centric dynamics, contrasting with global large-caps. In early 2026, with Fed easing and potential economic acceleration, the sector stands out for strength, driving small-cap performance amid broader market rotations.
Industrials
This sector (~15.8%) covers manufacturing, construction, infrastructure, transportation, and aerospace/defense firms. Small-cap industrials benefit from U.S.-focused operations, reshoring, government spending, and supply-chain shifts. They offer cyclical exposure, thriving on capital investment and business expansion during recoveries but vulnerable to cost pressures or slowdowns. Many supply larger entities or projects, providing leverage to economic upturns. With 2026 tailwinds like GDP growth, infrastructure focus, and lower rates, industrials remain a core driver of small-cap cyclicality and performance.
Notable Components
While the Russell 2000 encompasses thousands of companies, some notable constituents may periodically shift due to market dynamics. Examples of companies that might appear in the index (as of the last rebalancing) include:
AppLovin Corporation: A mobile marketing technology company that enables app developers to increase their revenue.
Buybuy Baby: A retailer specializing in baby products, illustrating consumer goods' presence in the index.
Chewy, Inc.: An online retailer of pet food and supplies reflecting a shift towards e-commerce in consumer discretionary.
Direct Investment in Individual Stocks

Investors can build a portfolio by purchasing shares of individual companies that make up the Russell 2000. While this approach can yield impressive returns, it also requires significant research and a thorough understanding of each company’s fundamentals and market trends.
Stock Selection: Investors should consider factors such as financial health, growth potential, competitive positioning, and industry trends when selecting stocks.
Diversification: Building a diversified portfolio within the Russell 2000 can mitigate risks associated with investing in individual stocks.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)

A more accessible and efficient way to gain exposure to the Russell 2000 is through exchange-traded funds. ETFs are designed to track the performance of the index by holding the same securities it encompasses. Some popular Russell 2000 ETFs include:
iShares Russell 2000 ETF (IWM): One of the most widely traded ETFs, it aims to replicate the performance of the Russell 2000 Index.
Vanguard Russell 2000 ETF (VTWO): This fund offers low expense ratios and seeks to provide investment returns that closely correspond to the index.
Schwab U.S. Small-Cap ETF (SCHA): Although not a direct tracker of the Russell 2000, it includes small-cap stocks, providing similar exposure.
Mutual Funds
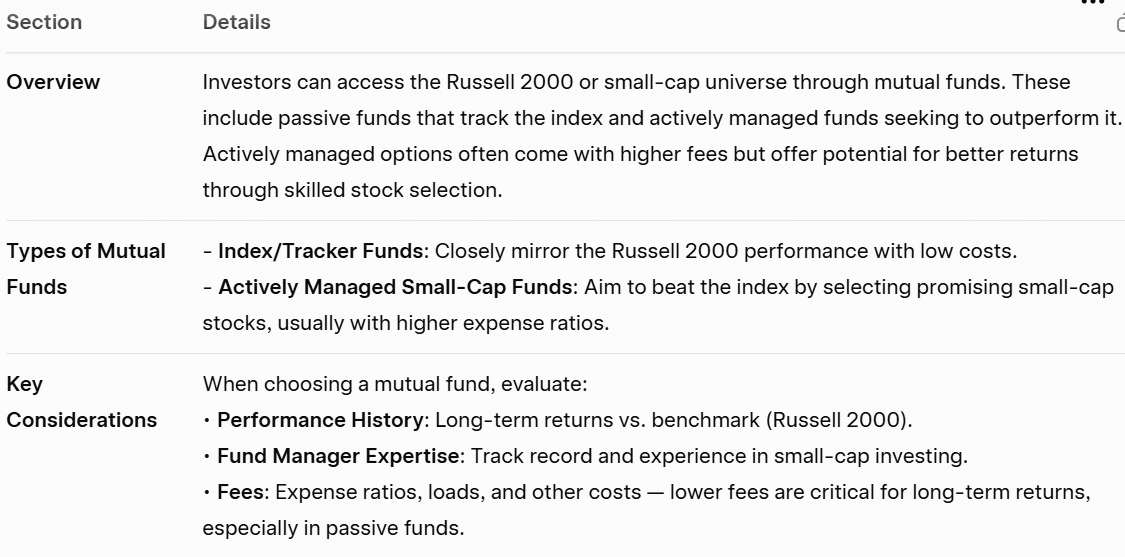
Investors can also choose mutual funds that focus on small-cap stocks or specifically those that aim to mirror the Russell 2000 Index. While actively managed mutual funds may have higher fees, they can provide opportunities to outperform the index.
Considerations for Mutual Funds: Investors should weigh performance history, fund manager expertise, and fees when selecting mutual funds.
Options and Futures

For more experienced traders, options and futures contracts on the Russell 2000 Index offer avenues for speculation and hedging.
Options Trading: Investors can buy call options if they anticipate the Russell 2000 will rise or put options if they expect it to decline. Options can be complex and carry significant risks, so thorough understanding is essential.
Futures Contracts: Futures contracts require buying or selling the underlying index at a predetermined future date and price. This type of trading can amplify potential gains but also losses due to leverage.
When trading or investing in the Russell 2000, several critical factors need consideration:
Market Conditions: Economic indicators, interest rates, and global economic events can significantly impact the performance of small-cap stocks.
Risk Tolerance: Small-cap stocks are often more volatile than large-cap stocks, so it is crucial to assess personal risk tolerance before entering the market.
Time Horizon: Investors should consider their investment time horizon—short-term trading and long-term investing may involve different strategies and risk assessments.

Research and Analysis
Stay Informed: Use financial news sources, stock analysis platforms, and economic reports to stay updated on market trends and stock movements within the index.
Fundamental Analysis: Examine the underlying fundamentals of companies in the index, such as earnings reports, revenue growth, and competitive positioning.
Technical Analysis: Utilize charts and technical indicators to identify trading patterns and trends that may present buying or selling opportunities.
Diversification Strategies
Broaden Your Portfolio: Invest in various industries and sectors within the Russell 2000 to mitigate sector-specific risks.
Consider Other Indices: While focusing on the Russell 2000, consider diversifying investments across other indices like the S&P 500 to balance overall portfolio risk.
Risk Management
Set Stop-Loss Orders: Minding the potential volatility of small-cap stocks, setting stop-loss orders can help limit losses in adverse market conditions.
Portfolio Rebalancing: Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
When it comes to trading or investing in the Russell 2000 Index, selecting a reliable broker is crucial. Markets.com is an excellent choice for traders looking to access index CFD trading.
User-Friendly Platform
Markets.com offers a sophisticated yet user-friendly trading platform that accommodates both novice and seasoned traders. Users can easily navigate the interface, access analytical tools, and execute trades seamlessly.
Diverse Trading Instruments
In addition to the Russell 2000 Index, Markets.com provides access to a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks, commodities, cryptocurrencies, currencies, and more. This diversification allows investors to explore various trading opportunities.
Educational Resources
Markets.com provides a wealth of educational materials, including webinars, articles, and tutorials, helping traders enhance their knowledge and skills. These resources can be particularly beneficial for beginners seeking to understand index trading.
Comprehensive Research Tools
With comprehensive research tools, including real-time market data and analysis, Traders can make informed decisions. This feature is essential for analyzing market trends and managing strategies effectively.
Competitive Fees
Markets.com offers competitive spreads and fees for CFD trading, helping maximize potential profits. This cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage for active traders.
Customer Support
Exceptional customer support is also a hallmark of Markets.com. Investors can access support through various channels, including live chat, email, and phone, ensuring they receive assistance when needed.
The Russell 2000 Index is an invaluable tool for investors looking to tap into the potential of small-cap companies. Understanding its composition, functionality, and the methods for trading can empower individuals to make informed investment decisions.
With thorough research, strategic planning, and risk management, trading the Russell 2000 Index can provide significant financial opportunities. Utilizing platforms like Markets.com enriches this experience, offering robust tools and resources that facilitate successful investing in this dynamic market segment.
As you embark on your journey in trading or investing in the Russell 2000 Index, remember to stay current with market developments, continuously educate yourself, and maintain a clear investment strategy that aligns with your personal financial goals.
Looking to trade index CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.