
Friday Nov 28 2025 09:16

11 min

CFD trading guide: Contracts for Difference (CFDs) have revolutionized trading by enabling market participants to speculate on price movements across a variety of asset classes without owning the underlying asset.
CFD trading tutorials: One of the most critical factors influencing CFD trading is market volatility. Volatility reflects the degree of variation in price movements over time and has profound effects on trading strategies, risk management, and overall trading experience.
This guide explores market volatility in detail—what it means, how it is measured, and why it is crucial for CFD traders. It also delves into the various ways volatility impacts CFD trading, offering actionable insights for traders at all experience levels.

What is Market Volatility?
Market volatility refers to the rate and magnitude of price changes in an asset or market over a given period. High volatility means prices fluctuate rapidly and often over large ranges, while low volatility indicates relatively stable prices with smaller, more gradual moves.
Volatility can be observed across all financial markets—equities, commodities, currencies, indices, and more. It reflects the uncertainty or risk about the size of changes in a security’s value.
Why Does Market Volatility Occur?
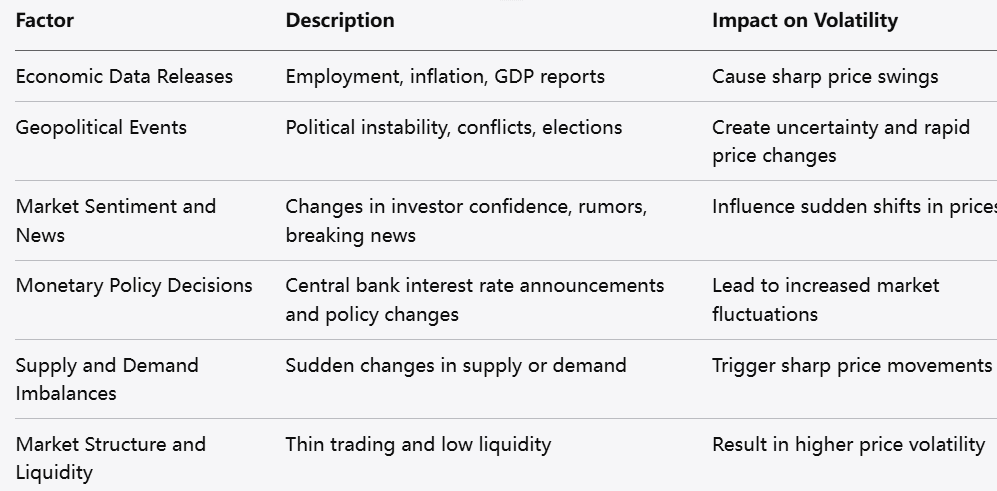
Several factors contribute to market volatility, including:
Economic data releases: Reports on employment, inflation, GDP, and other economic indicators often lead to price swings.
Geopolitical events: Political instability, conflicts, or elections create uncertainty.
Market sentiment and news: Shifts in investor confidence, rumors, or breaking news impact prices.
Monetary policy decisions: Central bank announcements on interest rates or policy changes influence volatility.
Supply and demand imbalances: Sudden shifts in supply or demand can cause sharp price movements.
Market structure and liquidity: Thinly traded assets tend to have higher volatility due to less liquidity.
Types of Volatility
Historical Volatility: The actual observed price movement of an asset over a past period.
Implied Volatility: The expected future volatility derived from options prices, reflecting market expectations.
Realized Volatility: Similar to historical volatility but often calculated more dynamically over shorter periods.
Common Volatility Metrics and Tools
Standard Deviation
Measures the dispersion of price changes from the average. A higher standard deviation signals greater volatility.
Average True Range (ATR)
Calculates the average of true ranges over a set period, showing how much an asset typically moves within a day.
Bollinger Bands
Bands plotted above and below a moving average expand and contract based on volatility, visually illustrating periods of high and low volatility.
Volatility Indexes (e.g., VIX for Equities)
Represent market expectations of future volatility, often called “fear gauges.”
Coefficient of Variation
Ratio of standard deviation to the mean, useful for comparing volatility across different assets.
Why Volatility Matters in CFD Trading
CFD trading involves speculating on price movements, so volatility directly affects both the potential rewards and risks. High volatility can create lucrative trading opportunities but also increases the likelihood of rapid losses.
Volatility and Leverage
CFDs are typically traded on margin, meaning traders only deposit a fraction of the total position value. While leverage magnifies potential gains, it also amplifies losses—especially in volatile markets where prices can move swiftly.

Trading Opportunities in Volatile Markets
Short-term trading: Volatility creates more frequent price swings, ideal for intraday traders looking for quick entry and exit points.
Breakout trading: Traders often watch for volatility spikes as breakout signals from established ranges or patterns.
Scalping: Rapid trades can benefit from small price movements amplified by volatility.
Challenges of Volatile Markets
Wider spreads: Increased volatility often leads brokers to widen bid-ask spreads, increasing costs.
Slippage: Rapid price changes can cause execution at worse prices than expected.
Emotional stress: Volatility can trigger impulsive decisions and emotional trading behavior.
Risk of margin calls: Leveraged positions can quickly erode equity during volatile swings.
Trading in Low Volatility Environments
Adjusting Position Sizes
In volatile markets, smaller position sizes help manage risk and prevent large drawdowns.
Setting Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels
Wider stop loss levels may be necessary to avoid getting stopped out by normal volatility, but this increases risk exposure. Conversely, tight stops in low volatility can avoid large losses but may trigger premature exits.
Using Volatility to Inform Entry and Exit Points
Traders can use volatility indicators to time entries when volatility is increasing, signaling potential price moves, or to exit when volatility drops, indicating possible consolidation.
Equity CFDs
Stock markets often experience volatility driven by earnings reports, sector news, and broad economic factors. Individual stocks may have higher volatility than indices.
Index CFDs
Indices generally have lower volatility than individual stocks but can be affected by macroeconomic events and geopolitical tensions.
Commodity CFDs
Commodities like oil and gold often show high volatility due to supply-demand changes, geopolitical risks, and global economic shifts.
Forex CFDs
Currency pairs vary in volatility; major pairs tend to be less volatile than exotic or emerging market currencies, influenced by monetary policy and economic data.
Stay Informed
Keeping abreast of economic calendars, news events, and geopolitical developments helps anticipate volatility spikes.
Choose the Right Trading Style
Match trading approaches to market volatility conditions. For example, use trend-following strategies in trending high volatility markets and range-bound strategies in quieter periods.
Use Demo Accounts
Practice trading strategies in simulated environments with varying volatility to understand how they perform.
Managing Emotions
Volatility can trigger fear and greed, leading to impulsive decisions. Maintaining discipline and following a trading plan is vital.
Avoiding Overtrading
High volatility may tempt traders to make excessive trades, increasing transaction costs and risk.
Developing Patience
Waiting for clear signals, rather than chasing price moves, helps mitigate emotional mistakes.

Trading Platforms
Most CFD trading platforms provide built-in volatility indicators and customizable alerts.
News Feeds and Economic Calendars
Real-time information helps traders prepare for upcoming volatility events.
Automated Trading Systems
Algorithmic and expert advisor systems can help execute trades based on volatility parameters without emotional bias.
Case Studies: Volatility in Action
Volatility During Major Economic Events
Examples include central bank announcements, GDP releases, or geopolitical crises triggering sharp price swings and trading opportunities.
Volatility in Crisis Periods
Market crashes or crises often produce extreme volatility, illustrating both risk and potential for traders who manage positions carefully.
Market volatility will always be an inherent feature of financial markets. For CFD traders, mastering volatility is fundamental to crafting resilient trading plans that balance risk and reward. By understanding volatility’s nature, adapting strategies accordingly, and managing emotions effectively, traders can improve their confidence and performance in the dynamic world of CFD trading.
Looking to trade CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.