
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Sunday Jan 4 2026 08:41

21 min

How does Bitcoin (BTC/USD) work: Launched in 2009, Bitcoin introduced the world to blockchain technology and decentralized finance.
Bitcoin for beginners: This article will delve into how Bitcoin works, the technology behind it, its potential uses, and how to start investing in Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that operates outside the control of any central authority, differentiating it from traditional fiat currencies issued by governments. Launched in 2009 by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin utilizes blockchain technology to enable secure and transparent peer-to-peer transactions.
Key Characteristics of Bitcoin

To understand Bitcoin fully, it’s essential to grasp the underlying technologies and principles that make it function.
2.1. Blockchain Technology
At the heart of Bitcoin is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network.
Blocks: Each block in the blockchain contains a list of transactions. Once a block is filled with transactions, it is added to the chain, forming a chronological record.
Decentralized Network: The blockchain is maintained by a network of nodes that verify transactions and ensure consensus. This decentralized system prevents fraud and double-spending.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or erased. This characteristic adds an extra layer of security and trust.
2.2. Mining Bitcoins
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new Bitcoins are created and transactions are verified. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transactions.
Proof of Work: Bitcoin uses a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW). This requires miners to expend computational energy to find a hash that meets certain criteria.
Block Rewards: When a miner successfully adds a block to the blockchain, they receive a reward in the form of newly minted Bitcoins along with any transaction fees included in the block.
Difficulty Adjustment: The difficulty of mining adjusts roughly every two weeks to ensure that new blocks are added to the blockchain approximately every ten minutes.
2.3. Transactions and Wallets
To send and receive Bitcoin, users need a digital wallet. Bitcoin wallets can be software-based (hot wallets) or hardware-based (cold wallets).
Wallet Address: Each wallet has a unique address, which is a string of letters and numbers that users can share to receive Bitcoin.
Private Keys: Wallets also contain private keys, which are secret codes needed to authorize transactions. Keeping private keys secure is crucial, as anyone with access to them can control the associated Bitcoins.
Understanding Bitcoin's economic model is essential for investors looking to navigate the market.
3.1. Supply and Demand
Like any asset, Bitcoin's price is influenced by supply and demand dynamics.
Scarcity: Bitcoin’s capped supply creates a scarcity effect. As more people recognize Bitcoin's value, demand increases, potentially driving prices up.
Investment Demand: Institutional interest and retail investments in Bitcoin contribute to its demand. Developments such as the adoption of Bitcoin by companies and financial institutions can significantly impact its price.
3.2. Halving and Its Implications
Bitcoin undergoes a process known as "halving," which occurs approximately every four years, reducing the block reward miners receive by half.
Reduction in Supply: Halving events reduce the rate at which new Bitcoins are mined, furthering the scarcity principle. This typically leads to increased prices, as demand remains constant or grows.
Historical Price Trends: Previous halving events have resulted in substantial price increases in the months and years following the halving, although not without volatility.
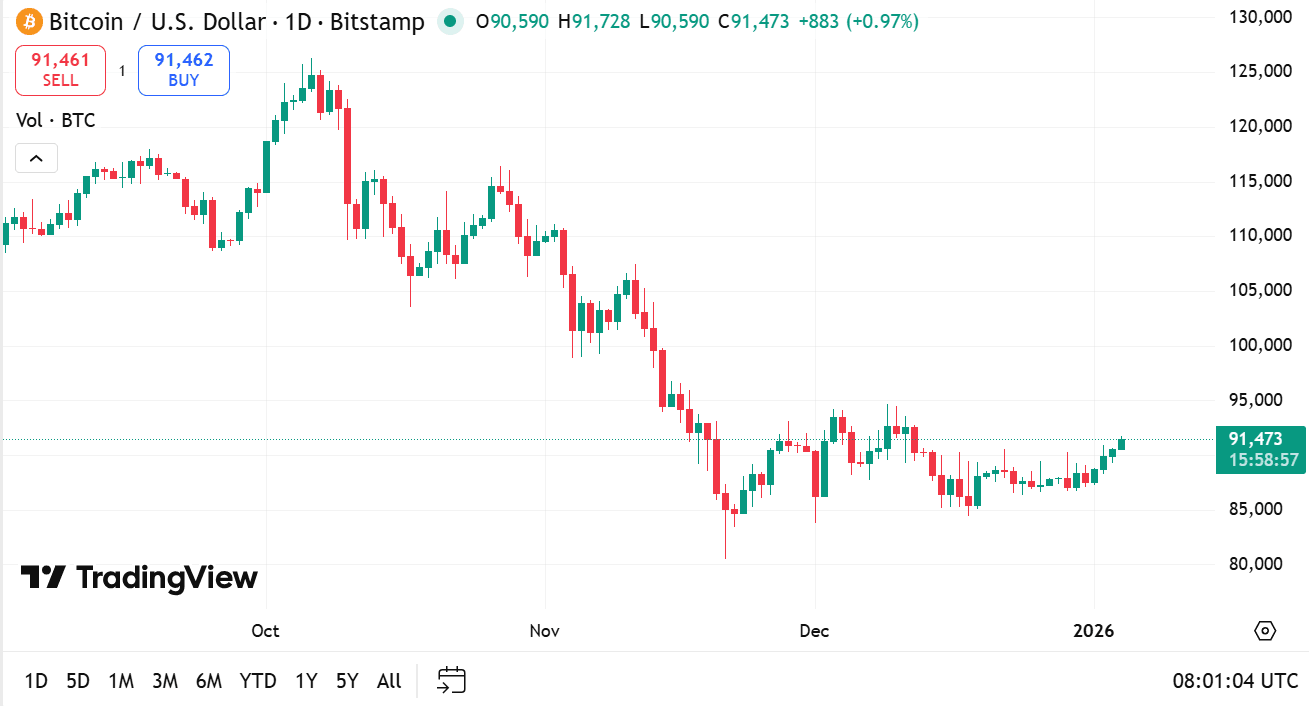
source: tradingview
Bitcoin offers several advantages that attract users and investors.
4.1. Decentralization
One of Bitcoin’s main advantages is its decentralized nature. This eliminates the need for banks or third-party intermediaries, empowering individuals to control their finances.
Lower Fees: Peer-to-peer transactions can incur lower fees compared to traditional banking systems, especially for international transfers.
Censorship Resistance: Decentralization helps protect against censorship and allows users to transact freely without governmental or institutional interference.
4.2. Safety and Security
Bitcoin's security stems from its robust underlying technology.
Cryptography: Transactions are secured through cryptographic algorithms, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access or alter transaction data.
Transparency and Auditability: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, allowing for complete transparency and enabling independent audits.
4.3. Global Accessibility
Bitcoin can be accessed from anywhere in the world with internet connectivity.
Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin can empower unbanked populations by providing access to financial services without the need for traditional banking infrastructure.
Transnational Transactions: Bitcoin enables seamless payments across borders, removing barriers associated with currency conversion and international fees.
While Bitcoin has many advantages, potential investors should also be aware of the various risks and challenges.
5.1. Volatility
Bitcoin's price is notoriously volatile, with significant fluctuations common over short periods.
Market Sentiment: Bitcoin prices can react dramatically to market sentiment, news events, or regulatory changes, leading to rapid wealth accumulation or loss.
Short-Term Trading Risks: This volatility can make short-term trading risky and may require traders to have advanced strategies and risk management techniques.
5.2. Regulatory Concerns
The regulatory landscape surrounding Bitcoin continues to evolve.
Uncertain Regulations: Governments worldwide are still determining how to approach cryptocurrencies, leading to uncertainty. Regulations can dramatically impact Bitcoin's usability and price.
Tax Implications: In many jurisdictions, Bitcoin investments are subject to capital gains tax. Investors should understand the tax implications associated with buying, holding, or selling Bitcoin.
5.3. Security Threats
Although Bitcoin is secure by design, it is not immune to security threats.
Hacking Risks: Cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets can be vulnerable to hacking, which can result in substantial losses for investors.
Phishing Attacks: Users may fall victim to phishing scams, where attackers trick individuals into providing their private keys or wallet credentials.

Trading Bitcoin through Contracts for Difference (CFDs) provides an opportunity to speculate on Bitcoin's price movements without owning the actual cryptocurrency. This method offers advantages such as leverage and the ability to short-sell, making it appealing for many traders. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to get started with Bitcoin CFDs.

With your account funded and a solid strategy in place, you can begin trading Bitcoin CFDs:
Monitor the Market: Keep a close watch on Bitcoin’s price movements and any news that might impact its value. Utilize your broker's analytical tools for informed decision-making.
Execute Trades: When you identify a favorable trading opportunity, you can either open a long position (buy) if you anticipate a price increase or a short position (sell) if you expect a decline.
Assess Performance: Regularly review your trades to evaluate performance. Analyze the results to understand what strategies worked and where improvements can be made.
Bitcoin CFD trading offers a robust platform for individuals looking to engage with the cryptocurrency market. By selecting a regulated broker, understanding the mechanics of Bitcoin CFDs, developing a solid trading strategy, and practicing risk management, you can embark on a path toward successful trading.
As with any trading activity, inherent risks come with Bitcoin CFDs. Stay educated, remain informed about market dynamics, and continuously refine your strategies to thrive in this evolving landscape. With discipline and a careful approach, you can navigate the complexities of Bitcoin CFD trading effectively.
Choose a Regulated Broker
The first essential step is selecting a reputable and regulated broker. Opting for a regulated broker ensures that your trading activities are conducted securely and in compliance with industry standards. Here are some of the top brokers for Bitcoin CFD trading in 2026:



Open a Trading Account
After selecting a broker, you’ll need to open a trading account. This process generally involves registering online, verifying your identity by providing the necessary documents, and funding your account using different payment methods like bank transfers or credit cards.
It's crucial to grasp what Bitcoin CFDs are and how they function. A Contract for Difference allows traders to speculate on Bitcoin's price movements without actually owning it. When trading Bitcoin CFDs, you can profit from both increases and decreases in price, leveraging your trades to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. However, this comes with risks, as while leverage can amplify profits, it can also exacerbate losses.

Develop a Trading Strategy
Creating a well-defined trading strategy is vital for successful CFD trading. Consider these components when developing your strategy:
Market Research: Stay informed about Bitcoin’s market trends and significant news events. Utilize technical analysis tools to evaluate price charts for potential entry and exit points.
Risk Management: Employ risk management techniques to safeguard your investment. Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and determine the right position size based on your overall risk tolerance.
Psychological Preparedness: Cultivate mental resilience to manage the emotional challenges associated with trading. Set realistic expectations and avoid impulsive decisions based on market fluctuations.
Investing in Bitcoin can be straightforward if you follow a systematic approach.
6.1. Educate Yourself
Before diving into Bitcoin investment, take the time to educate yourself about the cryptocurrency landscape, including its fundamental concepts, potential risks, and market behavior.
Read Books and Articles: Numerous resources are available online and in libraries that provide detailed information about Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies.
Join Communities: Engaging with online communities such as forums or social media groups can help you stay updated and learn from experienced investors.
6.2. Choose a Bitcoin Wallet
Selecting the right wallet is critical for storing your Bitcoin safely.
Hot Wallets: These are connected to the internet and are convenient for daily transactions. However, they are more vulnerable to hacking.
Cold Wallets: These are offline wallets, such as hardware wallets, that provide a higher level of security for long-term storage.
6.3. Find a Cryptocurrency Exchange
To buy Bitcoin, you’ll need to use a cryptocurrency exchange, which facilitates the buying and selling of cryptocurrencies.
Reputable Exchanges: Research and select reputable exchanges with strong security measures, user-friendly interfaces, and ample liquidity.
KYC Procedures: Most exchanges require users to complete Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, including identity verification, before trading.

6.4. Making Your First Purchase
Once you've selected a wallet and exchanged, you can make your first Bitcoin purchase.
Funding Your Account: Transfer funds from your bank account or other sources into your exchange account.
Place an Order: Find the Bitcoin trading pair (e.g., BTC/USD), choose your order type (market or limit), and place your order.
6.5. Developing a Strategy
Establishing an investment strategy can help you manage your investments effectively.
Investment Horizon: Define whether you plan to hold Bitcoin short-term or long-term. Your strategy may differ based on your investment goals.
Dollar-Cost Averaging: Consider this method, where you invest a fixed amount regularly, regardless of market conditions. This approach can mitigate the impact of volatility.
Different investment strategies can be used to navigate the Bitcoin market successfully.
7.1. Buy and Hold
The buy-and-hold strategy entails purchasing Bitcoin and holding it for an extended period, regardless of short-term price fluctuations.
Long-term Growth: This approach is based on the belief that Bitcoin will appreciate significantly over time as more individuals and institutions adopt it.
Reduced Stress: By not actively trading, investors can avoid the stress associated with daily market fluctuations.
7.2. Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging involves investing fixed amounts of money into Bitcoin at regular intervals.
Risk Mitigation: This strategy reduces the impact of market volatility by averaging the purchase price over time.
Consistency: It encourages consistency in investing, making it easier to commit funds regularly without worrying about market timing.
7.3. Trading
Active trading can also yield profits for knowledgeable investors. Traders can take advantage of price fluctuations to buy and sell Bitcoin.
Technical Analysis: Traders often use technical analysis to identify price trends, support and resistance levels, and potential entry and exit points.
High-Risk Strategy: Trading requires a solid understanding of market dynamics and comes with higher risks, including potential losses.
Once you invest in Bitcoin, effective management and storage are essential to safeguard your holdings.
8.1. Types of Wallets
Selecting the type of wallet that best suits your needs is crucial for managing your Bitcoin safely.
Software Wallets: Easy to use for transactions but may be vulnerable due to their online nature. Examples include mobile wallets and desktop wallets.
Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store your Bitcoin offline, providing a high level of security against hacking.
8.2. Security Best Practices
Implementing security best practices ensures the safety of your Bitcoin investments.
Use Strong Passwords: Ensure that your wallet and exchange accounts have strong, unique passwords and consider enabling two-factor authentication.
Backup Your Wallet: Regularly back up your wallet data to prevent loss due to device failure or loss. Store backups securely, away from your primary device.

The future of Bitcoin holds significant potential, shaped by various factors affecting its adoption, regulation, and technological advancements.
1. Market Adoption
As Bitcoin gains acceptance among mainstream financial institutions, businesses, and individuals, its utility and value could further increase.
Institutional Investment: Growing interest from institutional investors indicates confidence in Bitcoin as a viable asset class.
Payment Acceptance: More businesses are beginning to accept Bitcoin as a form of payment, enhancing its practical utility.
2. Technological Developments
Innovations in technology can enhance Bitcoin’s scalability, security, and efficiency.
Lightning Network: This payment protocol aims to enable faster and cheaper Bitcoin transactions, potentially increasing its adoption for everyday transactions.
Upgrades and Forks: Ongoing developments in Bitcoin's underlying technology may result in enhancements that improve usability and performance.
3. Regulatory Environment
The regulatory landscape will continue to evolve as governments seek to establish frameworks for cryptocurrency.
Legislation: Clear regulations can provide a solid foundation for Bitcoin’s growth, boosting investor confidence and potentially reducing volatility.
Global Standards: International cooperation on cryptocurrency regulations may lead to more consistency and security in the market.
Investing in Bitcoin presents an intriguing opportunity, characterized by both potential rewards and risks. Understanding how Bitcoin works, the underlying technology, its economic model, and the factors influencing its price can help investors make informed decisions.
As you embark on your journey into Bitcoin investment, remember to conduct thorough research, choose secure wallets, and adopt effective investment strategies tailored to your financial goals. By staying informed and adapting to changes in the market, you can position yourself for success in this evolving landscape.
Looking to trade bitcoin CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.